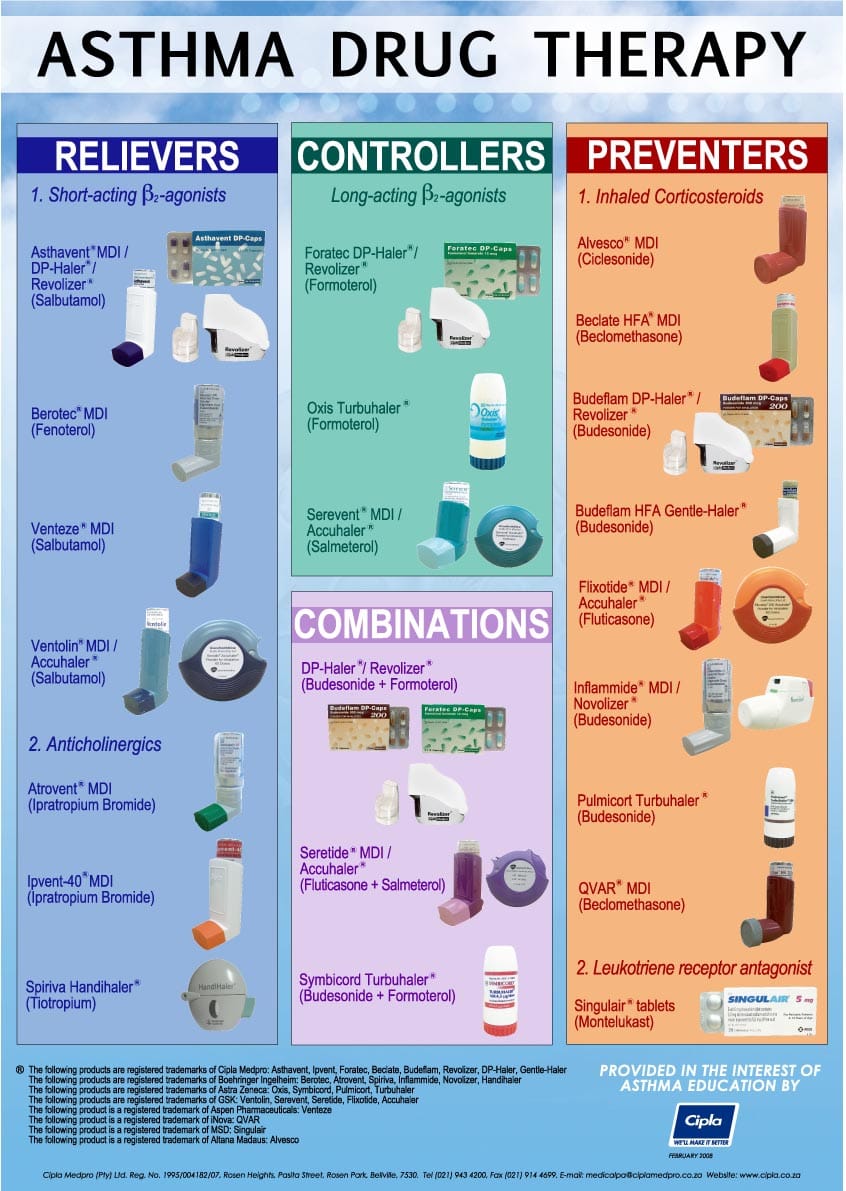
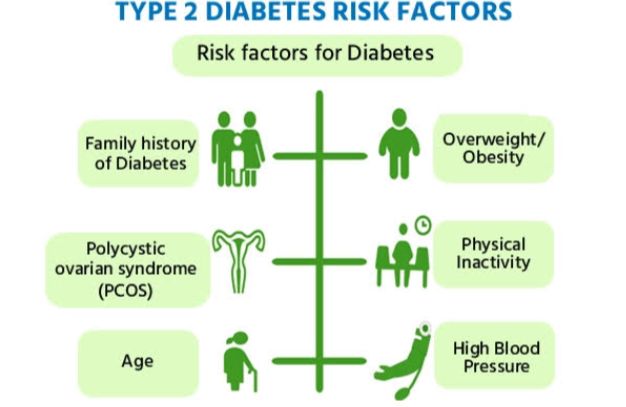
Medicines used to treat high blood pressure include:
Diuretics. These help remove sodium and water from the body. They are often the first medicines used to treat high blood pressure.
Your doctor will recommends a diuretic based on your blood pressure measurements and other health conditions, such as kidney disease or heart failure. Commonly used diuretics are chlorthalidone, hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide) and others.
A common side effect is frequent urination which may lead to hypolalemia. If you have low potassium (hypokalemia), your provider may recommend a potassium-sparing diuretic that contains triamterene.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. These drugs help relax blood vessels. Examples include lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril), benazepril (Lotensin), captopril etc.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). These drugs also relax blood vessels. They include candesartan (Atacand), losartan (Cozaar) etc.
Calcium channel blockers. These drugs help relax the muscles of the blood vessels and may also slow your heart rate. They include amlodipine (Norvasc), diltiazem (Cardizem, Tiazac) and others.
Don't eat or drink grapefruit products when taking calcium channel blockers. Grapefruit increases blood levels of certain calcium channel blockers, which can be dangerous. Always consult your doctor.
Other medicines sometimes used to treat high blood pressure
If you're having trouble reaching your blood pressure goal with combinations of the above medicines, your provider may prescribe:
Alpha blockers. These medicines reduce nerve signals to bloodd vesels. They include doxazosin (Cardura), prazosin (Minipress) and others.
Alpha-beta blockers. Alpha-beta blockers block nerve signals to blood vessels and slow the heartbeat. They reduce the amount of blood that must be pumped through the vessels. Alpha-beta blockers include carvedilol (Coreg) and labetalol (Trandate).
Beta blockers. These medicines reduce the workload on the heart and widen the blood vessels. This helps the heart beat slower and with less force. Beta blockers include atenolol (Tenormin), metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol-XL, Kapspargo sprinkle etc.
Aldosterone antagonists. These drugs may be used to treat resistant hypertension. Examples are spironolactone (Aldactone) and eplerenone (Inspra).
Renin inhibitors. Aliskiren (Tekturna) slows the production of renin, an enzyme produced by the kidneys that starts a chain of chemical steps that increases blood pressure.
Due to a risk of serious complications, including stroke, you shouldn't take aliskiren with ACE inhibitors or ARBs.
Vasodilators. These medicines stop the muscles in the artery walls from tightening. This prevents the arteries from narrowing. Examples include hydralazine and minoxidil.
Central-acting agents. Examples include clonidine (Catapres, Kapvay).
Treating resistant hypertension
You may have resistant hypertension if:
- You take at least three different blood pressure drugs, including a diuretic. But your blood pressure remains stubbornly high.
- You're taking four different medicines to control high blood pressure. Your care provider should check for a possible second cause of the high blood pressure.
Having resistant hypertension doesn't mean your blood pressure will never get lower. Your Doctor can determine the cause, and a more effective treatment plan can be created.
Treating resistant hypertension may involve many steps, including:
- Changing blood pressure medicines to find the best combination and dosage.
- Reviewing all your medicines, including those bought without a prescription.
- Checking blood pressure at home to see if medical appointments cause high blood pressure. This is called white coat hypertension.
- Eating healthy, managing weight and making other recommended lifestyle changes.