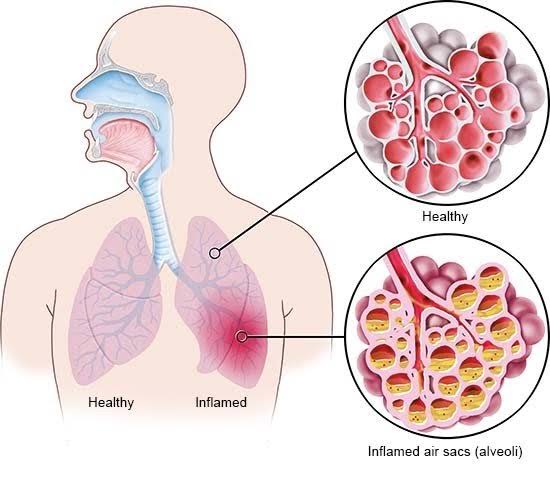
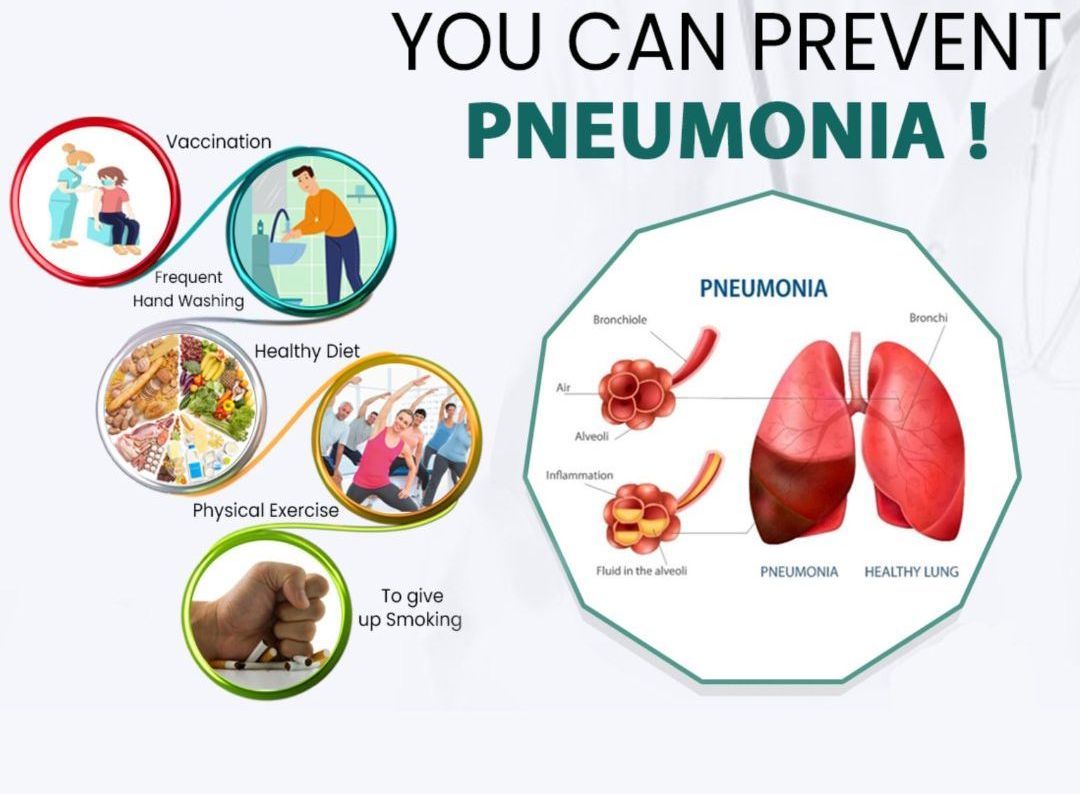
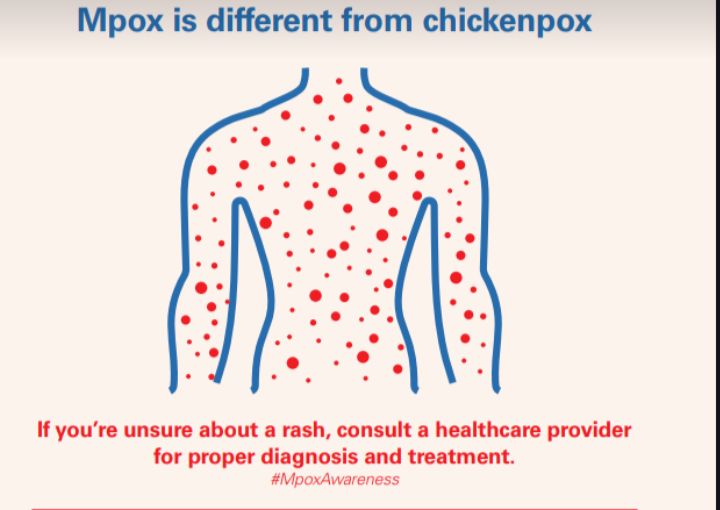
Pneumonia in Children
•Pneumonia is more common in younger children.
•The most affected age are children younger than 2 years since their immune system is still underdeveloped.
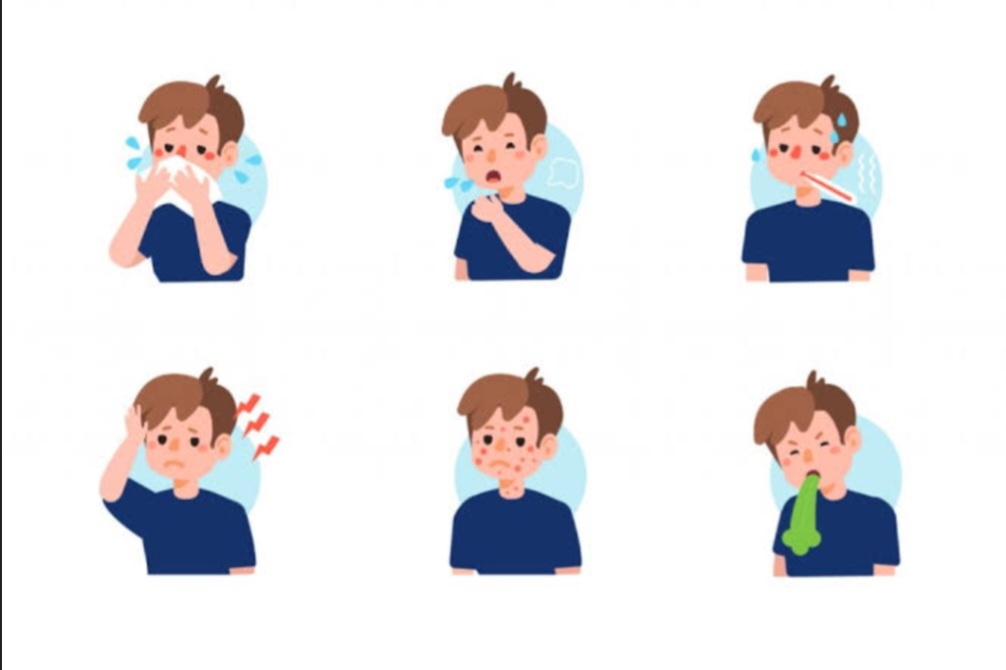
•Infants with pneumonia commonly show symptoms such as poor feeding, irritability, trouble breathing, retractions, hypoxemia (presents with symptoms such as headache, bluish skin and difficulty breathing), grunting and cough.
•Other major symptoms include; fever, dehydration and chest congestion.
•Always consult your healthcare provider on treatment for the child’s cough since over the counter cough remedies are not recommended.
•Ensure the child is given prescribed medication promptly.
•While recovering from pneumonia, the child should stay hydrated by taking enough fluids and get adequate rest.
•Furthermore, parents should protect their children from household air pollution, smoke and other irritants.
•The parent or care giver should maintain good hygiene and avoid any interaction between their child and individuals showing signs of respiratory illnesses or flu like symptoms.
•Ensure the child get exclusive breast feeding and complementary diet
Pneumonia in Adults
•Older children, adolescent and adults show the common signs of pneumonia.
•More specific symptoms include fever, headache, chest pain, cough, fatigue.
•In Adults who have other underlying conditions such as heart and lung diseases, pneumonia can be life threatening.
•Find the general tips on signs, symptoms, causes, complications, prevention, treatment etc. on our other tips on Pneumonia.
•Adults without underlying health conditions usually experience mild symptoms.
•However, proper treatment is recommended to avoid any risk of developing complications or getting re-infected.
Pneumonia in the Elderly
•People aged 65 years and more are vulnerable to pneumonia infection.
•As people age their immune system weaken.
•Additionally, the elderly are more likely to have chronic health conditions which increase their risk for pneumonia and other respiratory illnesses.
•The common symptoms among the elderly include; fatigue and general weakness, confusion or delirium, inability to do daily tasks, loss of appetite, cough, chest pain and other common pneumonia symptoms
•They may also experience worsening of an existing health condition.
•Always ensure proper diagnosis is done when you notice such symptoms among the elderly.
•Since the disease may progress much faster among the elderly, close care which mostly includes hospitalization is needed.
•If the recovery is done at home, ensure that they take their medication promptly, have good nutrition, they take enough fluids and get enough rest.
•Additionally, ensure any existing health condition is properly managed.