Understanding Asthma: Types, Causes, Signs & Symptoms, and Medication
What is Asthma
The word "asthma" is a Greek word which means “short breath”.
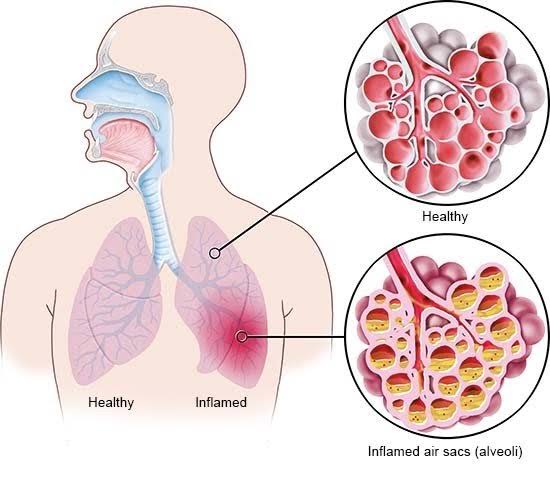
Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs that affects the airways (the tubes that carry air to and from the lungs).
It makes breathing difficult by causing bronchoconstriction (squeezing of the airways hence causing less air to pass through) or by causing inflammation (swelling of the lining of the airways which may lead to formation of mucus hence blocking air from passing through)
In general asthma leads to difficulty in breathing.
Types of Asthma
There are different types of asthma from mild to moderate to severe asthma.
Mild or intermittent asthma involves symptoms occurring less frequently in a week. In mild asthma, the lung tests appear normal unless the person is having an asthma attack or episode.
In moderate asthma, the symptoms occur almost on a daily basis. The symptoms affect the individual’s participation in activities. The lung test appear abnormal.
Severe asthma or severe acute asthma can be a medical emergency condition that calls for immediate attention of the doctor.
Asthma can also be classified depending on what triggers it. Asthma triggers can be an allergen or not. Therefore , it can be classified as either allergic or non-allergic.
Allergic asthma is triggered by exposure to allergens such as pollen, dust, animal dander, mold, latex, foods such as peanuts, dairy, fish or egg etc.
Non-allergic asthma is triggered by other factors that are not allergens such as extreme or cold weather, stress, and other illnesses such as flu, air irritants, and some medications. As a result, asthma can be classified as drug-induced asthma and occupational asthma (occurs in people who work around chemical fumes and other air irritants)
Exercise induced asthma occurs when the individual develops an asthmatic episode when engaging in physical activities and can occur for all the types of asthma.
Causes of Asthma
The exact cause of asthma is unknown. However, some people are genetically inclined to react to certain substances. Such substances are called asthma triggers.
Allergic asthma is caused by production of immune substances (such as immunoglobulin E) when the person is exposure to allergens. The tendency to produce such immune substances is genetic (run in families)
Non allergic (intrinsic) asthma is caused by other factors that are not allergens.
Signs & Symptoms of Asthma
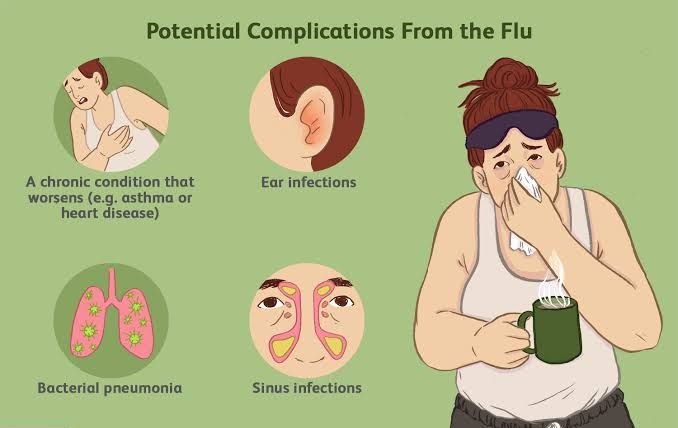
Asthma symptoms vary from mild to severe. They can occur as occasional attacks and inconveniences (asthma episodes or attacks) or can be life threatening such as in severe bronchial asthma (status asthmaticus).
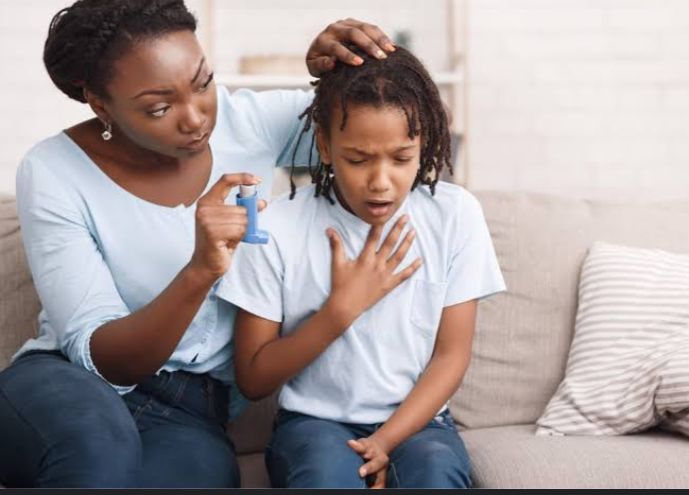
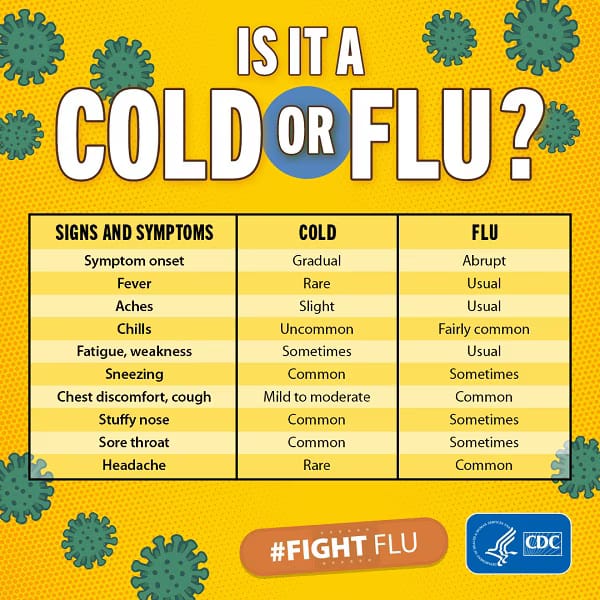
Common symptoms of asthma include wheezing (whistling sound made while struggling to breathe), coughing, and shortness of breath, chest tightness or chest pain.
Coughing and wheezing signs may worsen when the person has a respiratory virus such as cold or flu.
Additionally, asthma symptoms vary from person to person. Some may have asthma symptoms all the time while others may only experience attacks when engaging in activities or when doing exercise.
Diagnosis of Asthma
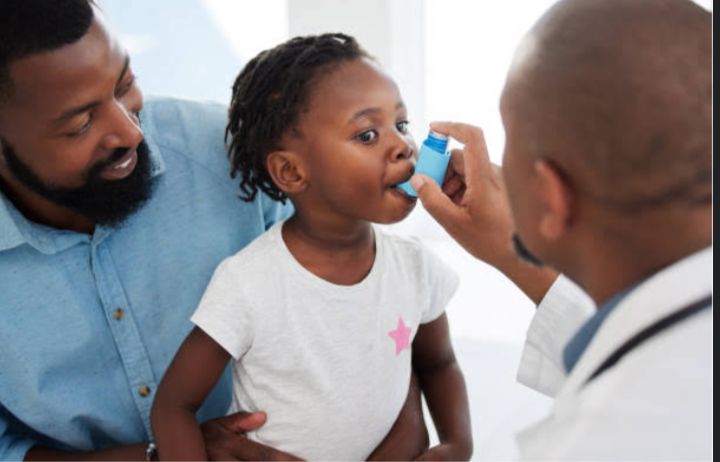
Respiratory diseases normally have similar signs, therefore for accuracy, your doctor should conduct a thorough medical history and breathing tests. The common breathing test for asthma is Spirometry which is a type of pulmonary function test. It entails measuring the amount of oxygen a person inhales, how much oxygen they exhale and how quickly they exhale.
Other tests include the Bronchial Challenge Test (BCT), FeNO test which your Doctor may decide to explore.
Your Doctor may opt for other additional test to rule out other lung conditions.
Medication used for Asthma
It is important to note that there is no cure for asthma
However asthma can be controlled by use of various medicines.
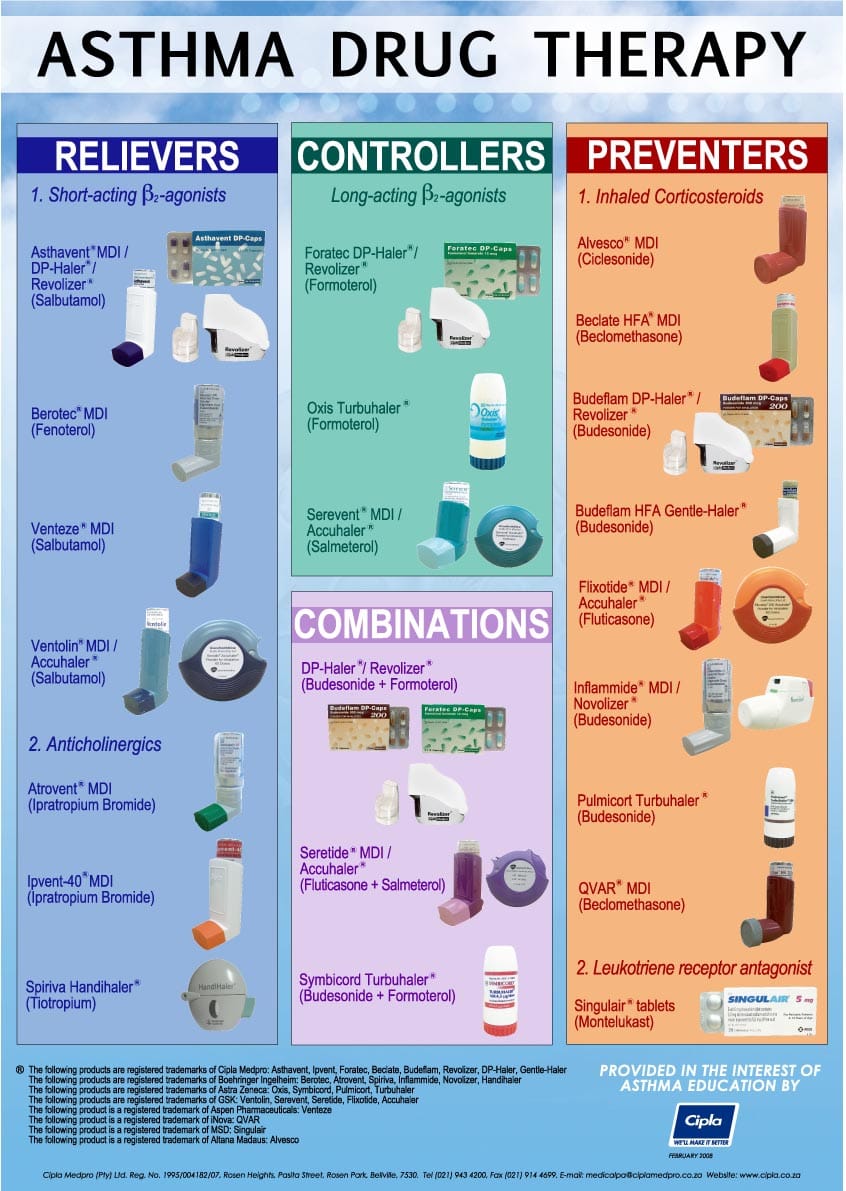
Since asthma leads to majorly bronchospasm (narrowing /squeezing of the airways), the medications used cause opening of the airways to allow air to flow hence allow for normal breathing. The drugs that is mostly used to manage asthma are called bronchodilators since they dilate (open) the airways.
Asthma medication can be for long term management or short term relief of asthma episodes.
In Short term management of asthma short acting bronchodilators such as albuterol are used.
Long term management of asthma utilizes drugs such as Formeterol (long acting bronchodilator), inhaled corticosteroids, Theophylline, Cromolyn, Omalizumab, Monteleukast.
The most common device used for asthma medicines is the INHALER. Additionally, NEBULIZERS are used especially for children. Inhalers and nebulizers are preferred over oral medication since they release the medicines directly to the airways.
Check out our tips on New Strategies in Treatment and Management of Asthma to learn more about how to manage asthma.