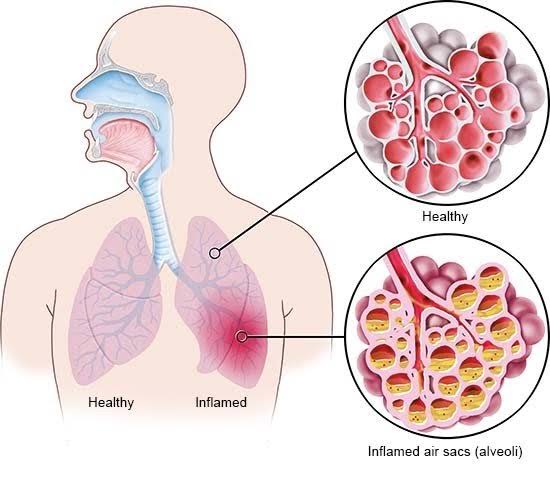
Today (MAY 12) is Women’s Health Check-Up Day at the start of Women’s health week. It's important to know that women's health is more than reproductive care. It spans mental, physical, and emotional well-being throughout life. Here are key health areas every woman should prioritize:
1. Don’t Miss Your Preventive Health Check-Ups
Routine check-ups and screenings are vital for early detection of chronic and reproductive conditions.
Annual wellness visits are crucial for preventive care.
Get regular screenings:
- Pap smear (every 3–5 years from age 21–65)
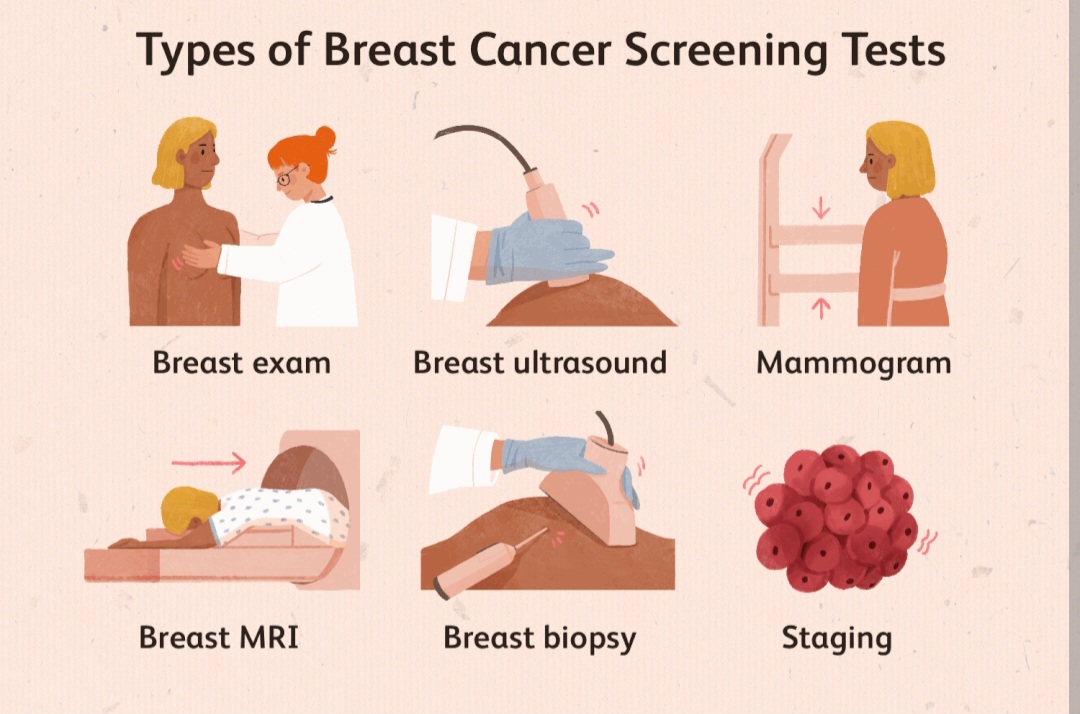
- Mammogram (every 1–2 years from age 40 or earlier based on risk)
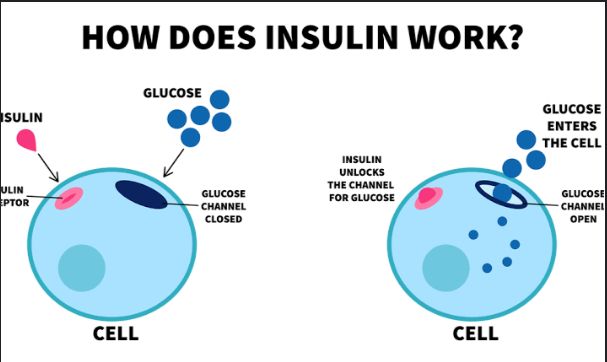
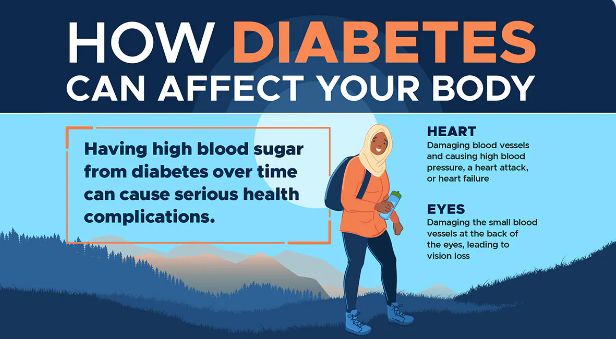
- Blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol checks
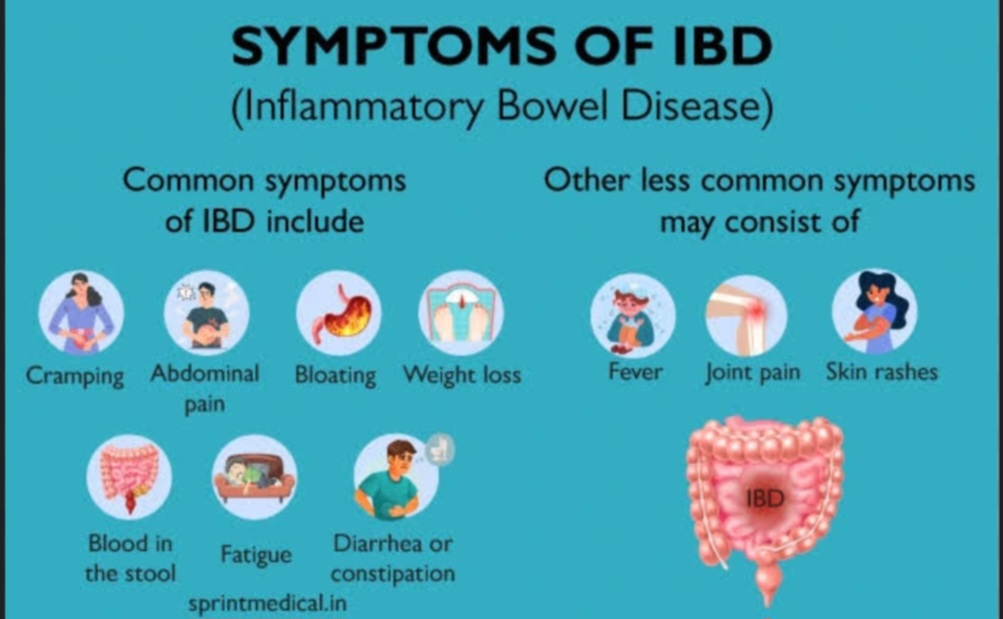
- Colon cancer screening (starting at age 45)
- Bone density test for postmenopausal women or those with risk factors
2. Prioritize Sexual and Reproductive Health
WHO emphasizes access to sexual and reproductive health as a human right.
Practice safe sex and get tested regularly for STIs (especially chlamydia, gonorrhea, and HIV).
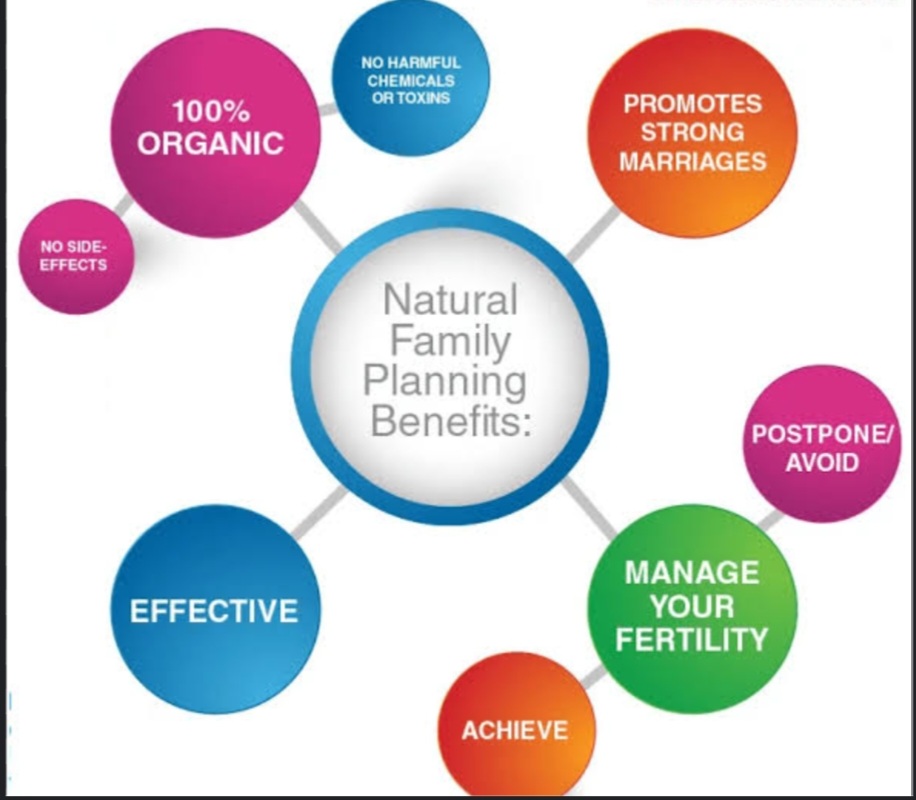
Discuss family planning options, fertility, menstrual health, or menopause concerns with a qualified provider.
HPV vaccination is strongly recommended for girls and young women (ages 9–26) to prevent cervical cancer.
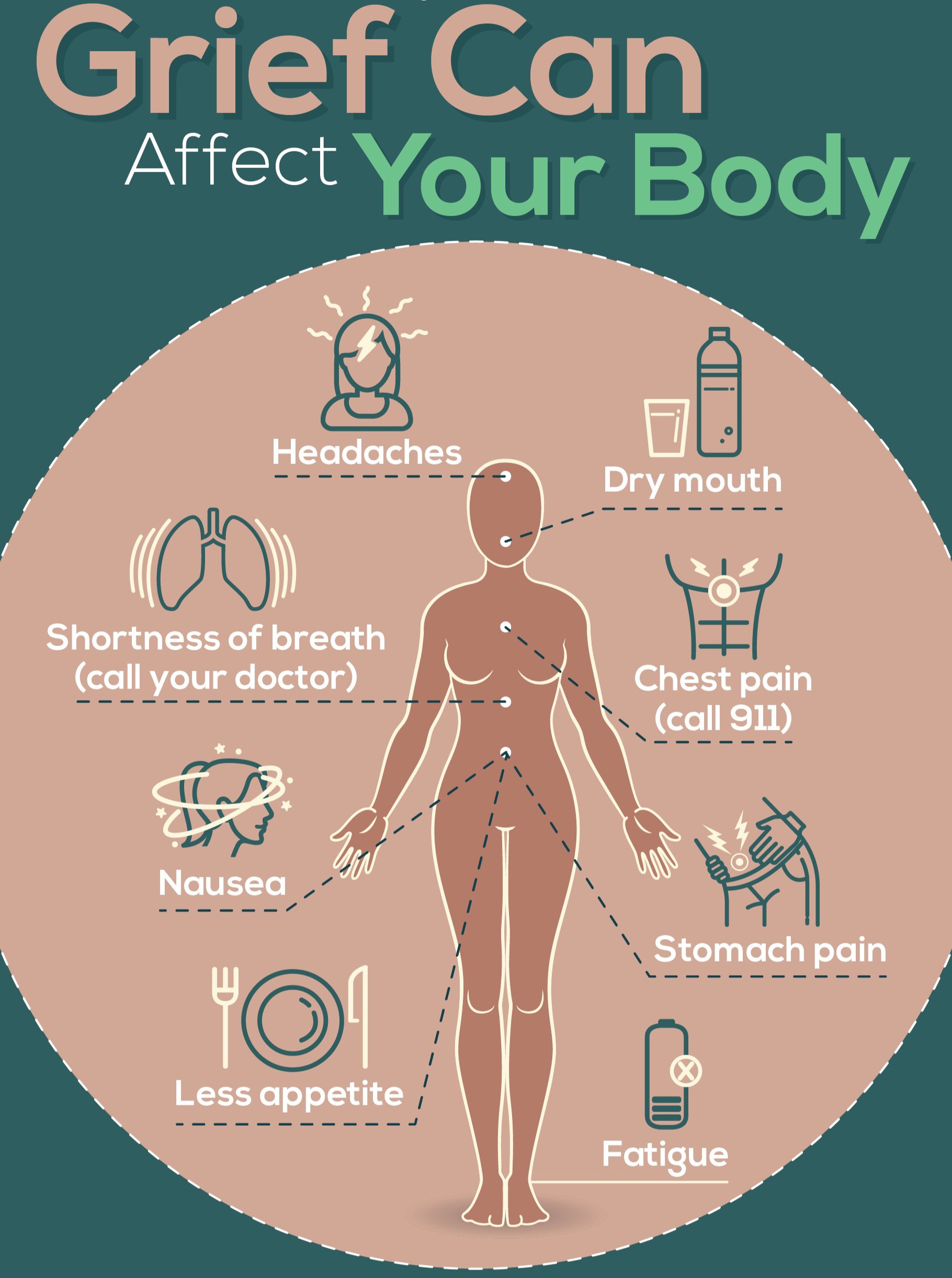
3. Protect Your Mental Health
Depression and anxiety are leading causes of illness among women.
According to WHO, Women are more likely to experience depression, anxiety, and stress due to hormonal shifts and societal factors.
Seek help early. Talk therapy, support groups, and medication (if needed) are effective.
Practice self-care: meditation, sleep, physical activity, and talking to a trusted friend or therapist.
4. Eat for Health, Not Just Weight
Balanced nutrition helps to reduce NCDs like diabetes and hypertension.
Eat more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and lean proteins.
Limit added sugar, saturated fats, and processed foods.
Ensure iron, folic acid, calcium, and Vitamin D intake — especially during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause.
Drink plenty of clean water — hydration supports hormonal balance and metabolism.
5. Get Active and Stay Moving
CDC recommends 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly.
Walk, dance, run, cycle, or try yoga — find what you enjoy.
Physical activity improves heart health, bone strength, mood, and reduces risk of obesity and chronic diseases.
6. Know Your Body: Early Signs Matter
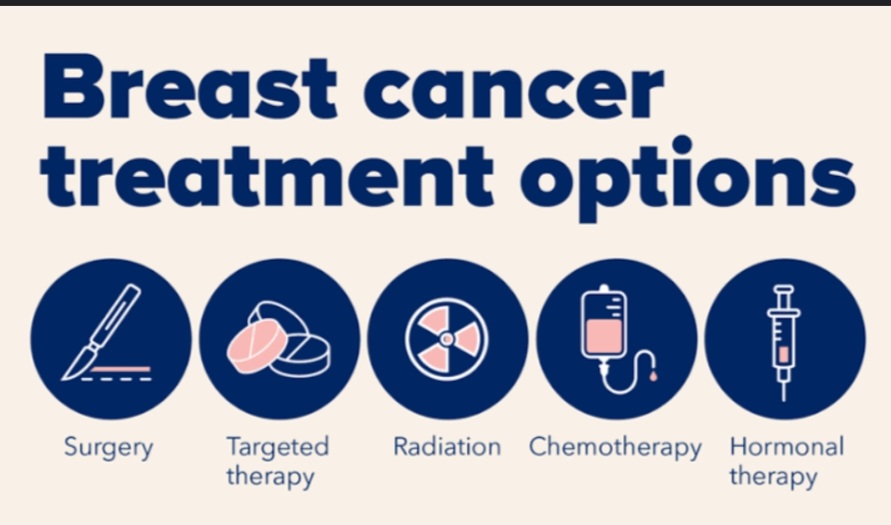
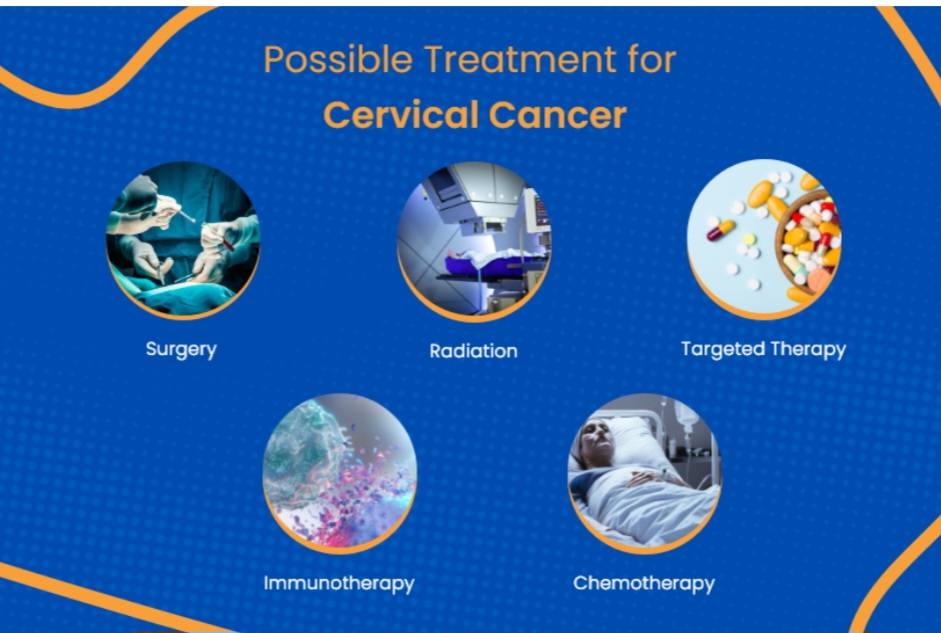
Early detection is vital in conditions like breast, cervical, and ovarian cancers.
Know what’s normal for your body. Watch for unusual changes:
Breast lumps or nipple discharge
Abnormal vaginal bleeding
Pelvic pain or bloating
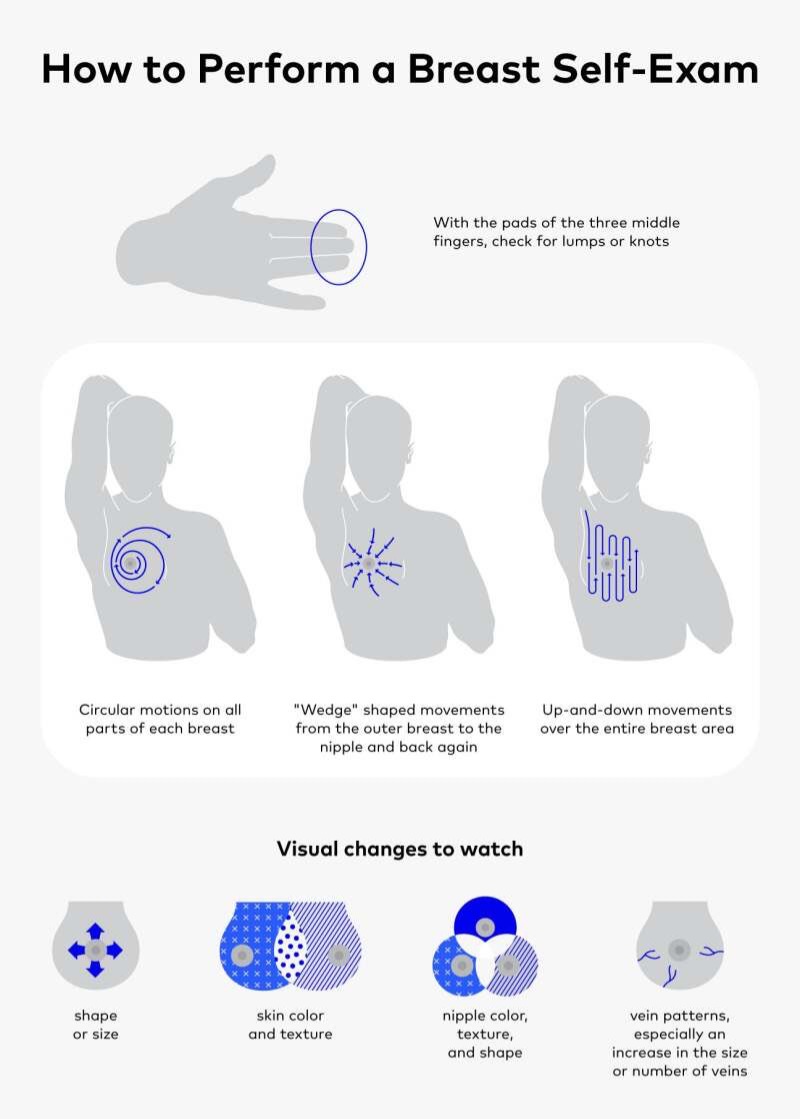
Perform monthly breast self-exams and consult a provider if anything feels off.
7. Stay Up-to-Date with Vaccinations
Vaccines as key to preventing disease.
Important vaccines for women include:
- HPV (prevents cervical cancer)
- Tetanus, Diphtheria, and Pertussis (Tdap)
- Influenza (annually)
- Hepatitis B, especially in high-risk areas
8. Understand Your Family Medical History
Genetics play a role in heart disease, diabetes, breast and ovarian cancer.
Share any family history with your healthcare provider for personalized risk assessments.
It can influence the type and frequency of screenings you need.
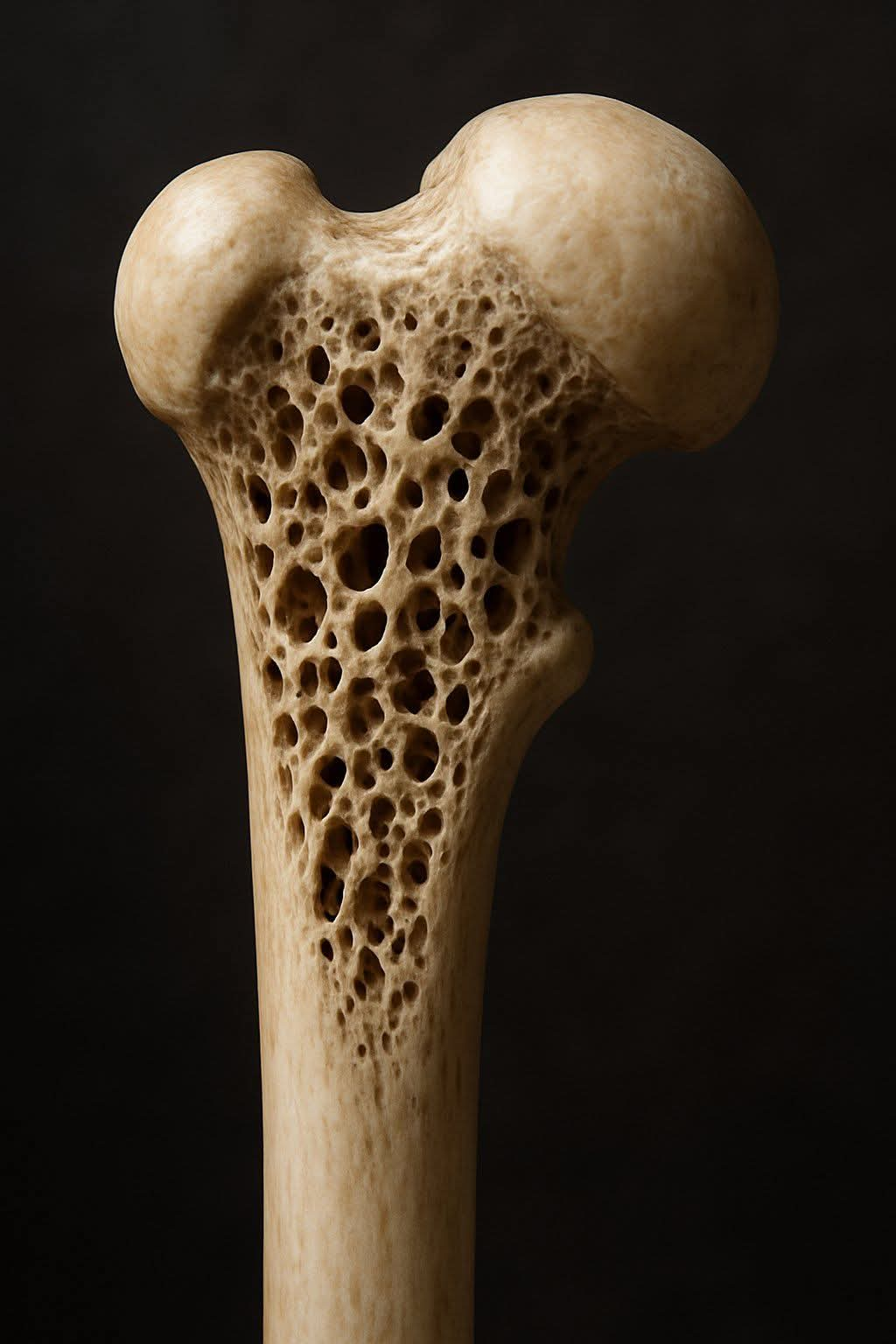
9. Care for Your Bones
Postmenopausal women are at higher risk of osteoporosis.
Include calcium-rich foods (dairy, leafy greens) and Vitamin D (sunlight, eggs, fortified cereals).
Strength training and weight-bearing exercises support bone density.
10. Balance Work, Rest, and Life
Lifestyle factors greatly influence women’s health outcomes. To cultivate balance, practice the following:
- Make time for adequate sleep (7–9 hours), stress relief, and mental breaks.
- Have Support systems — friends, family, or online communities — help maintain emotional resilience.
Your Health Is Your Power!